Floods are an often occuring natural phenomena in Europe, and while many floods have only minor socio-economic impact and environmental consequences, several floods especially in 2002 and 2005 turned in catastrophes, killing hundreds of people, displacing tens of thousands, and causing billions of euros in insured economic losses. In most cases, these disastrous consequences could have been minimized, had the right measures (e.g. land-use planning, flood plain mapping, river restoration) been applied. Thus, realizing the need for concerted action in 2006, the European Commission proposed the Directive on the assessment and management of flood risks (2007/60/EC), which entered into force in November 2007 and has to be transposed into national law by the end of 2009.
The overall aim of the Directive is to reduce and manage the risks that floods present to human health, the environment, cultural heritage and economic activity. It requires Member states to assess if any water courses and coastlines are at risk from flooding, to map the flood extend, assets, and humans at risk in these flood prone areas, and to take adequate and coordinated measures to reduce this flood risk (see Implementation and Time Schedule). The Directive also strengthens public participation by reinforcing the right to acces this information and to participate in the planning process. As this Directive is interconnected with water resources , regarding both quantity and quality as well as "good ecological status", it is to be carried out in coordination with the Water Framework Directive, especially through flood risk management plans and river basin management plans as well as concerted actions in support of public participation procedures in the preparation of these plans. River basins do not adhere to political boundaries, and Member States therefore have to coordinate their flood risk management practices in shared river basins, including third non-EU countries, not undertaking measures that would increase the flood risk in neighboring countries. They shoud also take into consideration long-term developments (e.g. climate change, population growth, urbanization) and sustainable land-use practices and incoorporate these in the adaptive flood risk management cycle.
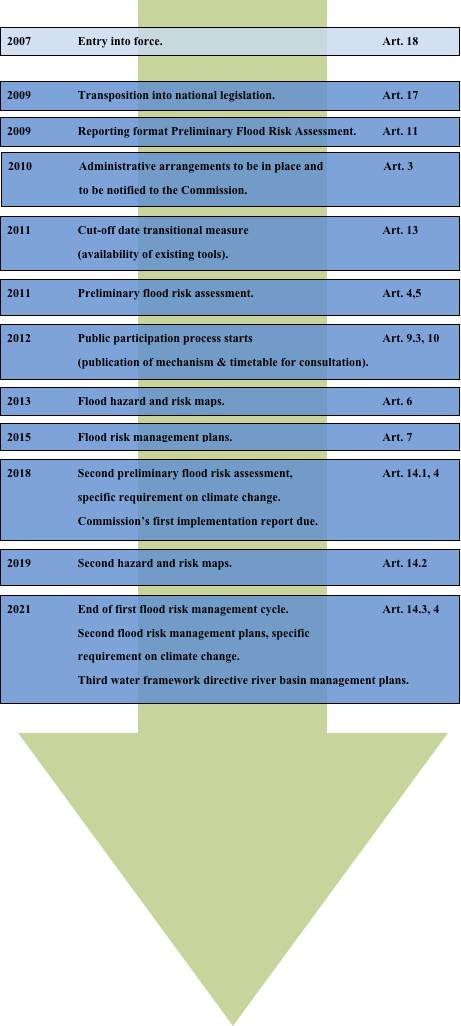
Implementation and time schedule
The Directive applies to all kinds of floods - rivers, lakes, flash floods, urban floods, coastal floods (storm surges and tsunamis) - on all the EU territory. Flood risk management under this Directive follows a three-stage approach whereby all Member States
As the nature of flooding is depending various factors that differ from country to country, the Directive allows considerable flexibility on objectives and measures in accordance with the subsidiarity principle of the EU. The above steps are to be reviewed every six years in a cycle coordinated and synchronised with the WFD implementation cycle. Similar to the implementation of the WFD, a Working Group on Floods has been established under the Common Implementation Strategy (CIS), which has published a document on their work programme and mandate for 2008-2009. The goal of this Working Group is to support the implementation of the directive and provide a platform for information exchange on flood risk management, promoting best practices and increasing the awareness of flood risks through wider stakeholder participation and more effective communication.
